In the world of software, there are two main categories: Open Source Software and Proprietary Software. Understanding the difference between these two types of software is essential for businesses, developers, and individual users. Each type comes with its own advantages, limitations, and use cases.
This guide will break down the key differences between open-source and proprietary software, helping you decide which one best suits your needs.
What is Open Source Software?
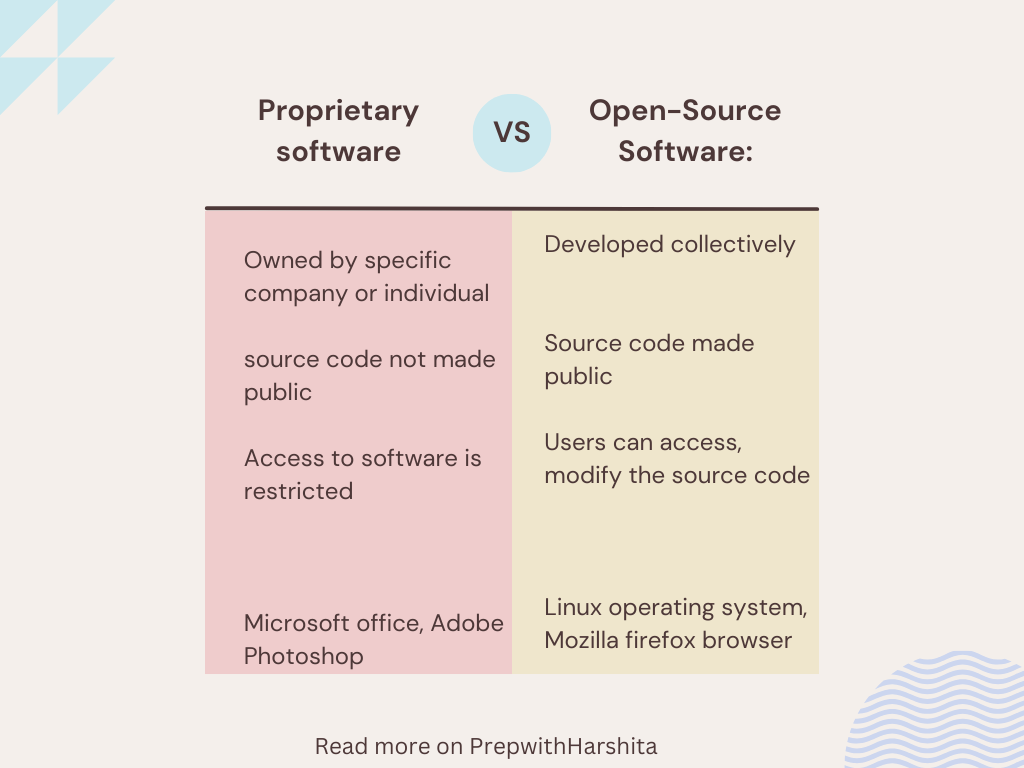
Open source software (OSS) is a type of software where the source code is freely available to the public. This means anyone can view, modify, and distribute the code without restrictions.
Key Features of Open Source Software:
- Free to use – Most open-source software is available at no cost.
- Modifiable – Users can customize and improve the software according to their needs.
- Collaborative Development – Open source projects are often maintained by a community of developers who contribute to improvements and bug fixes.
- No Licensing Restrictions – Users do not need a special license to install or share open-source software.
- Enhanced Security – Since the source code is accessible, developers worldwide can identify and fix security vulnerabilities faster.
Examples of Open Source Software:
- Android – The world’s most popular mobile operating system.
- Linux – A widely used operating system for servers, desktops, and embedded systems.
- Firefox – A fast and secure web browser.
- OpenOffice – A free alternative to Microsoft Office.
- GIMP – An open-source image editing tool.
- VLC Media Player – A free and open-source multimedia player.
What is Proprietary Software?
Proprietary software, also known as closed-source software, is software owned and controlled by a company or developer. Unlike open-source software, the source code is not publicly available, meaning only the original developers can modify or distribute it.
Key Features of Proprietary Software:
- Paid License Required – Users must purchase a license to use the software.
- Restricted Modification – The source code cannot be modified by users.
- Limited Installation – The software can only be installed on a certain number of devices as per the license agreement.
- Official Support & Updates – The software company provides technical support and regular updates.
- Strong Intellectual Property Protections – Companies retain full rights and prevent unauthorized modifications or redistribution.
Examples of Proprietary Software:
- Windows – Microsoft’s popular operating system.
- macOS – Apple’s operating system for Mac computers.
- Microsoft Office – A widely used office productivity suite.
- Adobe Photoshop – A professional image editing tool.
- Google Earth – A mapping and geographic exploration tool.
- Skype – A communication and video conferencing software.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary Software
| Feature | Open Source Software | Proprietary Software |
|---|---|---|
| Source Code | Available to the public | Not available to users |
| Development | Created through open collaboration | Developed by a company or closed team |
| Flexibility | Users can modify and customize | Users cannot modify or alter the software |
| Licensing | Free to use, often with open licenses | Requires a paid license to use |
| Security | More secure due to community-driven updates | Security updates depend on the vendor |
| Cost | Generally free | Users must pay for a license |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation and rapid improvement | Innovation is limited to company developers |
| Bug Fixes | Faster fixes due to a large developer community | Vendor is responsible for fixing issues |
| Intellectual Property | Limited protection | Strong intellectual property rights |
| Support | Community support, with some paid options | Official support from the company |
| Examples | Linux, Android, Firefox, VLC, OpenOffice | Windows, macOS, Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop |
Pros and Cons of Open Source Software
Pros:
- Free to use – No licensing costs, making it cost-effective.
- Highly customizable – Developers can modify and enhance features.
- Faster bug fixes and updates – Thanks to a large developer community.
- More secure – Transparency allows quick identification of vulnerabilities.
- Encourages innovation – Collaboration leads to continuous improvements.
Cons:
- Limited official support – Most open-source software relies on community support.
- Not always user-friendly – Some open-source tools require technical knowledge.
- Compatibility issues – May not always integrate smoothly with proprietary software.
Pros and Cons of Proprietary Software
Pros:
- Official support and maintenance – Customers receive technical assistance and updates.
- User-friendly interface – Designed for ease of use with built-in features.
- Comprehensive security – Companies ensure that software remains secure and updated.
- Full intellectual property protection – Protects company innovations.
Cons:
- Expensive – Requires purchasing a license, sometimes with additional subscription fees.
- Limited customization – Users cannot modify the software to fit their needs.
- Vendor dependency – Users rely on the company for updates and bug fixes.
- Installation restrictions – Licenses may limit the number of devices the software can be installed on.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choose Open Source Software If:
- You want free and customizable software.
- You have technical skills and can handle minor troubleshooting.
- You prefer collaborative development and community-driven improvements.
- Security and transparency in the code are important to you.
Choose Proprietary Software If:
- You need official support and regular updates.
- You prefer a user-friendly experience with built-in features.
- Security and data privacy are top concerns.
- You need professional tools for business, like Microsoft Office or Adobe Photoshop.
Final Thoughts
Both open-source software and proprietary software have their own benefits and drawbacks. Open-source solutions are great for users who value flexibility, cost savings, and customization, while proprietary software is better suited for those who need official support, enhanced security, and ease of use.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your needs, budget, and technical expertise. Whether you choose open-source or proprietary software, the goal is to find the best solution for your business or personal use.