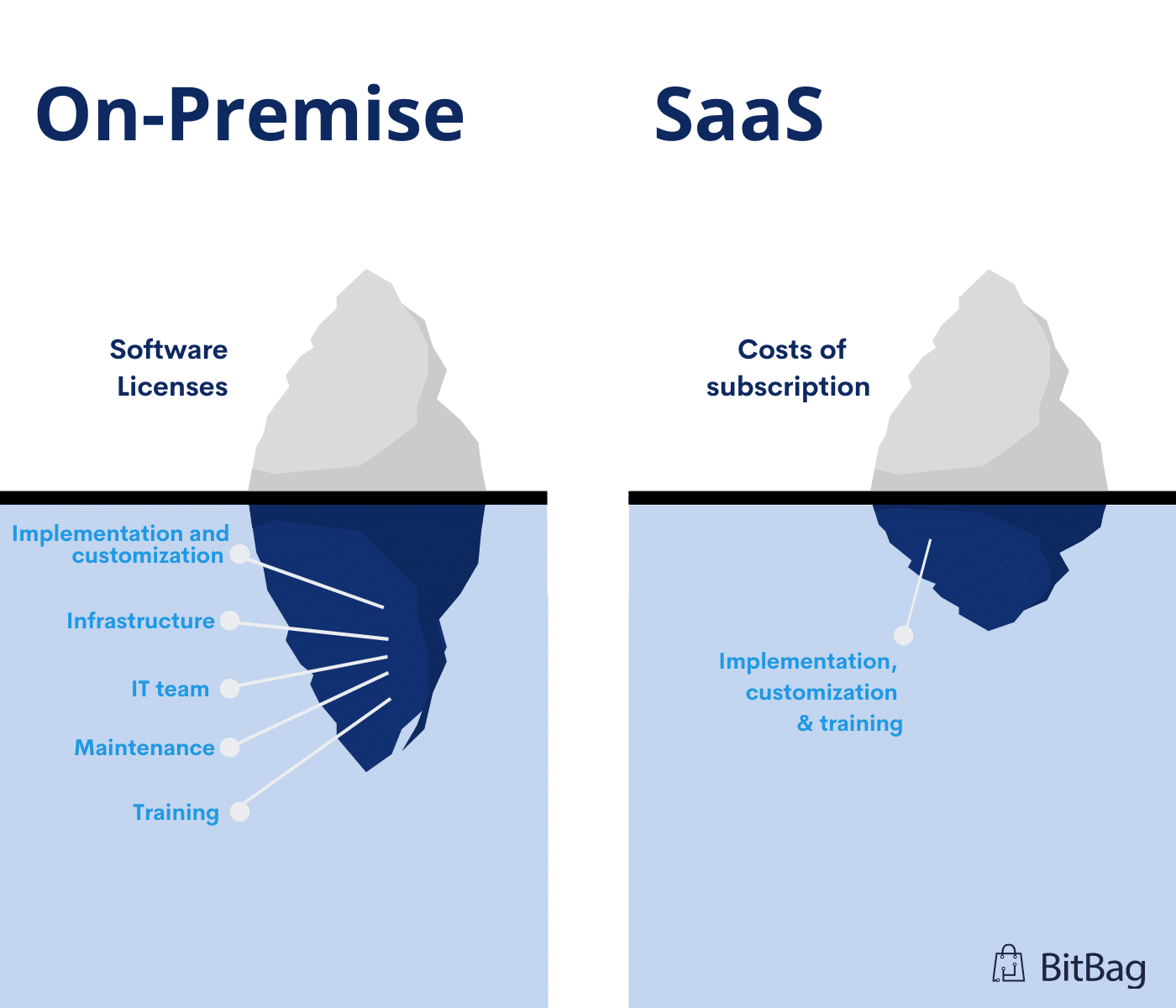
Choosing the right software solution for your business can be a tough decision. With so many factors to consider—cost, security, scalability, customization, and maintenance—it’s essential to understand the key differences between Software as a Service (SaaS) and On-Premises Software. Each model has its own advantages and challenges, making it crucial to select the one that best fits your needs.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications and data are hosted by a third-party provider and accessed via the internet. Instead of installing software on individual computers or servers, businesses subscribe to a service that handles all the technical aspects, including updates, security, and maintenance. Popular SaaS applications include Salesforce, Netflix, Slack, and Zoom.
What is On-Premises Software?
On-premises software is a traditional software model where businesses purchase a license to install and operate the software on their own hardware. This setup requires a dedicated IT team to manage maintenance, security, and updates. Companies using on-premises software have complete control over their infrastructure but must also bear the associated costs and responsibilities.
Benefits of SaaS
SaaS has gained popularity due to its flexibility, affordability, and ease of use. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
SaaS eliminates the need for expensive upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead of paying a large sum for a software license, businesses pay a monthly or annual subscription fee. This makes SaaS more budget-friendly, especially for startups and small businesses.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the biggest advantages of SaaS is its ability to scale with business needs. As your company grows, you can easily upgrade your subscription to accommodate more users or features. Unlike on-premises software, which often requires purchasing new hardware and software licenses, SaaS provides a seamless expansion experience.
3. Easy Maintenance and Updates
SaaS providers handle software updates, security patches, and maintenance, ensuring businesses always have access to the latest features and security measures. This eliminates the need for IT teams to manually update systems, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
4. Enhanced Security
Leading SaaS providers invest in robust security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. They often provide better data protection than many businesses can afford on their own.
5. Remote Accessibility
With SaaS, employees can access applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes it ideal for businesses with remote teams, multiple office locations, or employees who frequently travel.
6. Continuous Innovation
SaaS providers regularly release new features and improvements to stay competitive. Unlike on-premises software, which may require costly upgrades, SaaS users automatically benefit from the latest advancements without additional expenses.
Benefits of On-Premises Software
While SaaS offers many advantages, on-premises software remains the preferred choice for businesses requiring full control over their IT environment. Here’s why:
1. Full Data Control
With on-premises software, businesses have complete control over their data. This is crucial for companies handling sensitive or confidential information, such as healthcare providers, financial institutions, and government agencies.
2. No Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Since on-premises software is hosted locally, businesses can continue operations even if there’s an internet outage. This ensures uninterrupted access to critical applications and data.
3. One-Time Licensing Cost
Unlike SaaS, which requires ongoing subscription fees, on-premises software involves a one-time purchase. While maintenance costs still apply, some businesses prefer this model as it avoids long-term recurring payments.
4. Customization and Integration
On-premises software allows for deeper customization and integration with existing systems. Businesses with specific operational needs can modify software to fit their workflows more precisely.
SaaS vs. On-Premises: How to Choose the Right Option
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to choosing between SaaS and on-premises software. The decision depends on various factors, including:
1. Budget
- SaaS: Lower upfront costs, predictable subscription fees.
- On-Premises: High initial investment but no ongoing subscription fees.
2. Scalability
- SaaS: Easily scales with business growth.
- On-Premises: Requires purchasing additional hardware and licenses for expansion.
3. Accessibility
- SaaS: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- On-Premises: Limited to company-owned devices and network access.
4. Security and Compliance
- SaaS: Security handled by the provider, but businesses must ensure compliance with industry regulations.
- On-Premises: Full control over security but requires dedicated IT resources to maintain it.
5. Maintenance and Support
- SaaS: Maintenance, updates, and support are managed by the provider.
- On-Premises: Businesses are responsible for software updates, bug fixes, and IT support.
The Value of SaaS for Modern Businesses
For many businesses, SaaS presents a strong business case due to its quick deployment, lower costs, and minimal IT maintenance requirements. Additionally, SaaS providers often have highly skilled security teams that ensure better data protection compared to what many organizations could achieve independently.
Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Deployment Time: SaaS applications can be deployed much faster than on-premises software.
- Training and Support: SaaS providers usually offer extensive customer support and training.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based SaaS solutions provide built-in backup and redundancy to prevent data loss.
- Integration: SaaS applications are often designed for seamless integration with other cloud-based tools.
Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, SaaS and on-premises software each have their pros and cons. The best choice depends on your business’s unique needs, industry regulations, and budget.
- If you prioritize flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, SaaS is likely the better option.
- If your business requires strict data control, extensive customization, and independence from internet connectivity, on-premises software may be the way to go.
Regardless of your choice, always evaluate vendors carefully, considering security, compliance, and long-term value. The right software solution can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, productivity, and growth.
By understanding the key differences between SaaS vs. On-Premises Software, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your company’s goals and operational requirements. Whether you opt for a cloud-based SaaS solution or a traditional on-premises system, choosing the right software is crucial for long-term success.