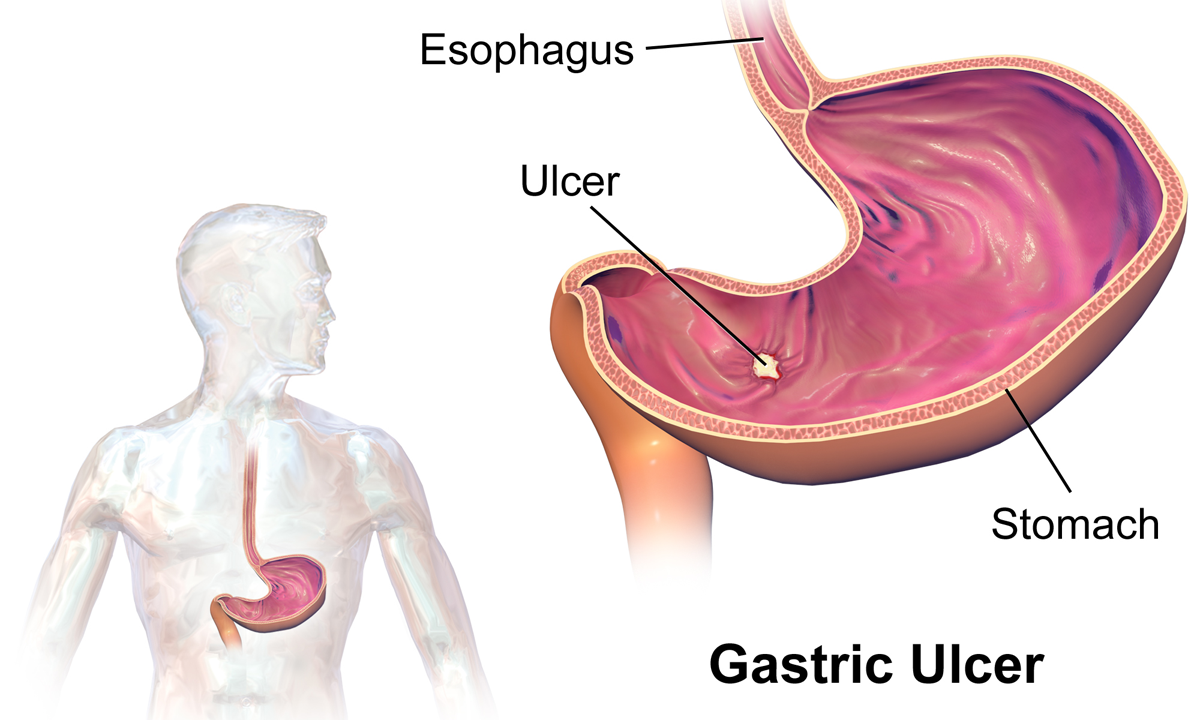
A gastric ulcer—commonly known as a stomach ulcer—is a painful sore in the stomach lining. It affects millions globally and, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. This guide provides in-depth insights into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of gastric ulcers.
What Is a Gastric Ulcer?
A gastric ulcer is a type of peptic ulcer that forms on the stomach’s inner lining due to an imbalance between digestive acids and protective mucus. According to Harvard Health, ulcers can result from bacterial infections or medication overuse.
Causes of Gastric Ulcers
1. H. pylori Infection
The most common cause is Helicobacter pylori, a bacteria that weakens the stomach’s mucosal lining, making it vulnerable to acid damage.
2. NSAIDs Overuse
Long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen or aspirin) can erode the stomach lining.
3. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking
Excessive alcohol consumption
Chronic stress
These may contribute or worsen ulcer symptoms.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing gastric ulcer symptoms early can prevent complications. Common signs include:
Burning stomach pain
Nausea or vomiting
Bloating or belching
Weight loss
Dark or bloody stools (in severe cases)
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, seek medical attention.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
Doctors may use endoscopy, a breath test for H. pylori, or stool antigen tests to confirm the ulcer and its cause.
Treatment Options
Antibiotics to eliminate H. pylori
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce stomach acid
Antacids for symptom relief
Lifestyle changes, such as reducing NSAID use, quitting smoking, and modifying diet
Tips for Prevention and Recovery
Avoid spicy, acidic, or fried foods
Eat smaller, frequent meals
Limit caffeine and alcohol
Manage stress through mindfulness or therapy
Following a treatment plan and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce recurrence.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing frequent stomach pain, unexplained weight loss, or vomiting blood, consult a gastroenterologist promptly. Early diagnosis leads to more effective treatment and prevents complications like internal bleeding or perforation.
Image Alt Text Suggestions:
“Stomach anatomy highlighting a gastric ulcer”
“Doctor discussing gastric ulcer treatment with patient”
“Healthy foods for ulcer-friendly diet”
