Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue, especially as men age. While it was once mainly treated by urologists, today, primary care doctors also help manage ED thanks to widely available medications like Viagra and Cialis. However, these drugs don’t work for everyone and don’t fix the root cause of ED. A full approach—looking at physical health, mental well-being, and lifestyle—often works better than just pills.
What Is Erectile Dysfunction?
ED is the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough for sex. It affects:
- 40% of men at age 40
- 70% of men at age 70
ED can be a warning sign of heart disease, diabetes, or poor circulation. It can also hurt self-esteem and relationships.
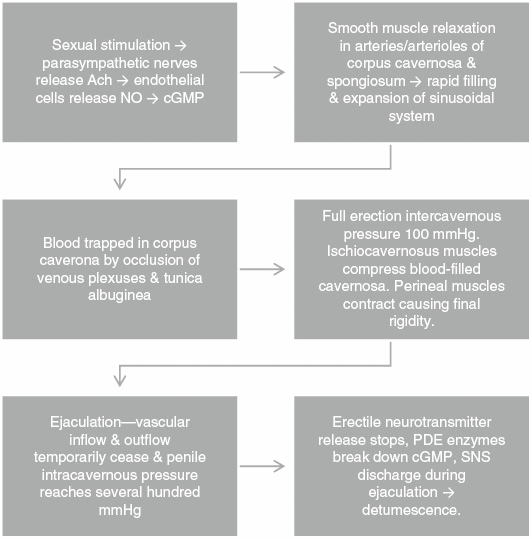
How Do Erections Work?
An erection happens when:
- Brain & Nerves – Sexual thoughts trigger signals from the brain and spinal cord.
- Blood Flow – Blood vessels in the penis relax, allowing more blood to flow in.
- Trapping Blood – Muscles and tissues trap the blood to keep the erection firm.
- Return to Normal – After ejaculation, blood flows out, and the penis softens.
If any part of this process fails—due to nerve damage, poor blood flow, or stress—ED can happen.
What Causes ED?
1. Psychological Factors
- Stress, anxiety, or depression
- Relationship problems
- Performance anxiety (worrying about sexual performance)
2. Physical Health Issues
- Heart disease & high blood pressure (poor blood flow)
- Diabetes (nerve and blood vessel damage)
- Low testosterone (affects sex drive and erections)
- Obesity & lack of exercise (linked to poor circulation)
3. Medications & Habits
- Antidepressants, blood pressure meds, and sedatives
- Smoking & heavy drinking
- Excessive porn use (can make real-life arousal harder)
How Is ED Diagnosed?
Doctors use:
✔ Medical history – Questions about health, medications, and sexual habits.
✔ Physical exam – Checking blood pressure, heart health, and the penis/testicles.
✔ Blood tests – Checking testosterone, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
✔ Questionnaires – Like the SHIM (Sexual Health Inventory for Men) to measure ED severity.
Treatment Options for ED
1. Lifestyle Changes (First Step!)
- Exercise – Improves blood flow and heart health.
- Healthy diet – Mediterranean-style eating (olive oil, fish, veggies) helps.
- Weight loss – Even losing 10–15 lbs can improve erections.
- Quit smoking & limit alcohol – Both harm blood vessels.
2. Oral Medications (PDE5 Inhibitors)
- Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), Levitra (vardenafil), Stendra (avanafil)
- How they work: Boost blood flow to the penis when sexually aroused.
- Side effects: Headaches, flushing, upset stomach (usually mild).
- Warning: Never take with heart medications containing nitrates (dangerous blood pressure drop).
3. Testosterone Therapy (If Levels Are Low)
- Helps if ED is due to low testosterone.
- Often combined with PDE5 inhibitors for better results.
4. Vacuum Erection Devices (Penis Pumps)
- A non-drug option that uses suction to create an erection.
- Works for 70% of men, but some find it awkward.
5. Penile Injections & Suppositories
- Injections (ICI): A small needle delivers medicine (alprostadil) directly into the penis.
- Urethral suppository (MUSE): A pellet inserted into the urethra.
- Pros: Works even when pills don’t.
- Cons: Can cause pain or priapism (prolonged erection).
6. Penile Implants (Surgical Option)
- For men who don’t respond to other treatments.
- Inflatable implants let men control when they have an erection.
- High satisfaction rates, but surgery has risks (infection, mechanical failure).
7. Therapy & Counseling
- Helps if ED is caused by stress, anxiety, or relationship issues.
- Sex therapy can improve confidence and communication with partners.
What Doesn’t Work?
- Herbal supplements (most lack strong scientific proof).
- Penile vein surgery (not recommended—poor long-term results).
- Shockwave therapy & stem cell treatments (still experimental).
Key Takeaways from the AUA Guidelines
ED is common and treatable.
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, quitting smoking) help.
PDE5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis) are the most common treatment.
Testosterone therapy works if levels are low.
Pumps, injections, and implants are options if pills don’t work.
Mental health support (therapy) can make a big difference.
If you’re struggling with ED, talk to your doctor. The right treatment can improve not just your sex life but your overall health too!
